Machining is a core manufacturing process characterized by high precision, high flexibility, and the ability to process complex parts.
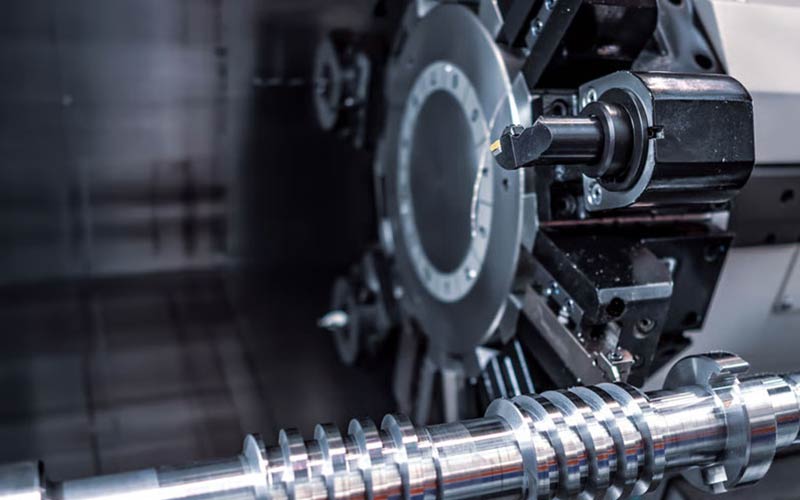
Machining is a manufacturing process that transforms metal or non-metal blanks into parts with specific dimensions, shapes, and surface quality through methods such as cutting, milling, turning, grinding, drilling, and boring. It is an important means of manufacturing high-precision and complex parts.
Machining is suitable for high-precision, complex structures and load-bearing parts, covering industries such as machinery, automotive, aerospace, energy, electronics, tools, and agricultural and construction machinery, meeting both single-piece customization and mass production needs.
Drive shafts, crankshafts, camshafts, rolling bearing shafts
Spur gears, helical gears, worm gears
Flywheels, gear discs, flanges
Pump bodies, valve bodies, machine casings, instrument housings
Complex curved surface parts, stepped shapes, grooves and holes, threads
Brackets, frames, connecting plates, supports
Capable of machining parts with extremely tight tolerances and stable dimensions.
Suitable for irregularly shaped parts, precision holes, threads, and complex surfaces.
Almost all metals and some non-metals can be machined.
Grinding and finishing processes can achieve smooth surfaces.
Suitable for small batches, custom parts, and rapid prototyping.
Can machine castings, forgings, or welded parts to finished products.
Get a free consultation from our casting experts now.
Almost all metals can be machined, such as carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, aluminum alloy, copper alloy, titanium alloy, high-strength steel, etc.; some engineering plastics, composite materials, and ceramics can also be machined.
Various complex structural parts such as shafts, gears, discs, housings, irregularly shaped parts, and load-bearing structural components.
Micrometer-level precision can be achieved, and the tolerance range varies depending on the processing equipment and process, generally ±0.01–0.1 mm.
A flat and smooth surface can be obtained. High surface quality requirements can be achieved with grinding, polishing, spraying, electroplating, or anodizing.
Yes, complex curved surfaces and precision irregularly shaped parts can be achieved through CNC milling, wire cutting, electrical discharge machining, and multi-axis machining.